简介
HPA(Horizontal Pod Autoscaling) 可以根据 CPU 利用率自动伸缩一个 ReplicaSet 或 Deployment 中的 Pod 数量
我们知道,初始Pod的数量是可以设置的,同时业务也分流量高峰和低峰,那么怎么即能不过多的占用K8s的资源,又能在服务高峰时自动扩容pod的数量呢,在K8s上的答案是Horizontal Pod Autoscaling,简称HPA 自动水平伸缩,这里只以我们常用的CPU计算型服务来作为HPA的测试,这基本满足了大部分业务服务需求。
案例一
# 为deployment资源web创建hpa,pod数量上限3个,最低1个,在pod平均CPU达到50%后开始扩容
# kubectl autoscale deployment web --max=3 --min=1 --cpu-percent=50
# 我们现在以上面创建的deployment资源web来实践下hpa的效果
# 1.首先用web的yaml配置并增加资源分配配置增加
# vim web.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: web
name: web
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: web
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: web
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:1.21.6
name: nginx
resources:
limits: # 因为我这里是测试环境,所以这里CPU只分配50毫核(0.05核CPU)和20M的内存
cpu: "50m"
memory: 20Mi
requests: # 保证这个pod初始就能分配这么多资源
cpu: "50m"
memory: 20Mi
更新web资源:
# kubectl apply -f web.yaml
deployment.apps/web configured
然后创建hpa:
# kubectl autoscale deployment web --max=3 --min=1 --cpu-percent=50
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/web autoscaled
# 等待一会,可以看到相关的hpa信息(K8s上metrics服务收集所有pod资源的时间间隔大概在60s的时间)
# kubectl get hpa -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
web Deployment/web <unknown>/50% 1 3 1 39s
web Deployment/web 0%/50% 1 3 1 76s
我们来模拟业务流量增长,看看hpa自动伸缩的效果:
# 设置Service,实现负载均衡的效果
kubectl expose deployment web --port=80 --target-port=80 --name=web
# 查看Service IP
root@k8s-master01:~# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.68.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 7d20h
nginx ClusterIP 10.68.106.223 <none> 80/TCP 141m
web ClusterIP 10.68.254.9 <none> 80/TCP 11m
# 我们启动一个临时pod,来模拟大量请求
# kubectl run -it --rm busybox --image=registry.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/acs/busybox:v1.29.2 -- sh
# while :;do wget -q -O- http://10.68.254.9;done
# 等待2 ~ 3分钟,注意k8s为了避免频繁增删pod,对副本的增加速度有限制
# kubectl get hpa web -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
web Deployment/web 0%/50% 1 3 1 11m
web Deployment/web 102%/50% 1 3 1 14m
web Deployment/web 102%/50% 1 3 3 14m
# 看下hpa的描述信息下面的事件记录
# kubectl describe hpa web
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
...
Normal SuccessfulRescale 62s horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 3; reason: cpu resource utilization (percentage of request) above target
好了,HPA的自动扩容已经见过了,现在停掉压测,观察下HPA的自动收缩功能:
# 可以看到,在业务流量高峰下去后,HPA并不急着马上收缩pod数量,而是等待5分钟后,再进行收敛,这是稳妥的作法,是k8s为了避免频繁增删pod的一种手段
# kubectl get hpa web -w
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE
web Deployment/web 102%/50% 1 3 3 16m
web Deployment/web 0%/50% 1 3 3 16m
web Deployment/web 0%/50% 1 3 3 20m
web Deployment/web 0%/50% 1 3 1 21m
案例二
cat hpa-deploy.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: hpa-web
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hpa-web
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hpa-web
spec:
containers:
- name: hpa-web
image: gcr.io/google_containers/hpa-example
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
limits:
cpu: 200m
memory: 200Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hpa-web
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: hpa-web
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80

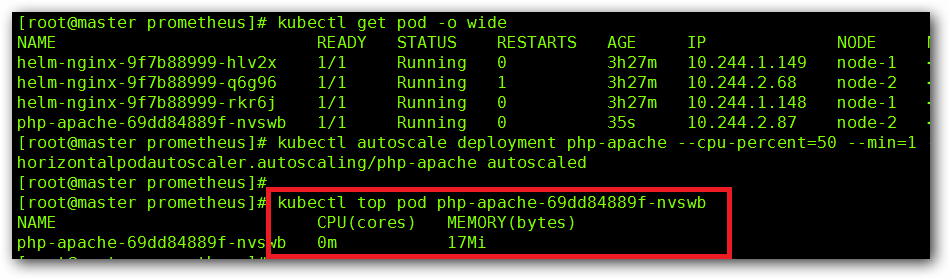
创建 HPA 控制器 - 相关算法的详情请参阅这篇文档:http://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/design-proposals/horizontal-pod-autoscaler.md#autoscaling-algorithm
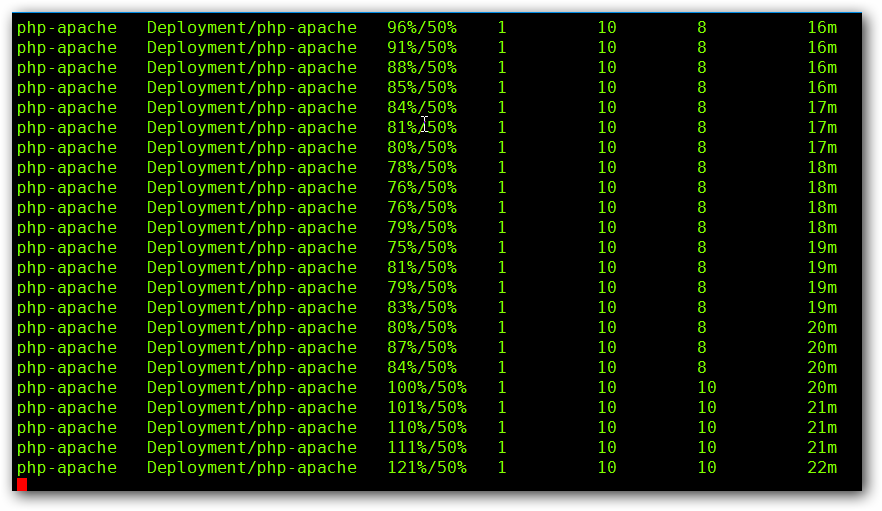
kubectl autoscale deployment hpa-web --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
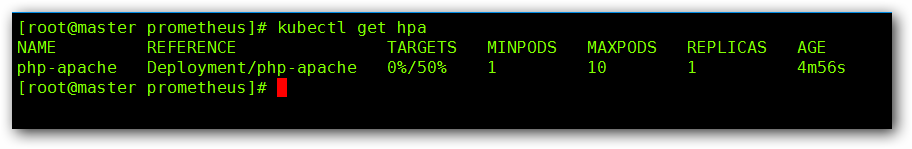
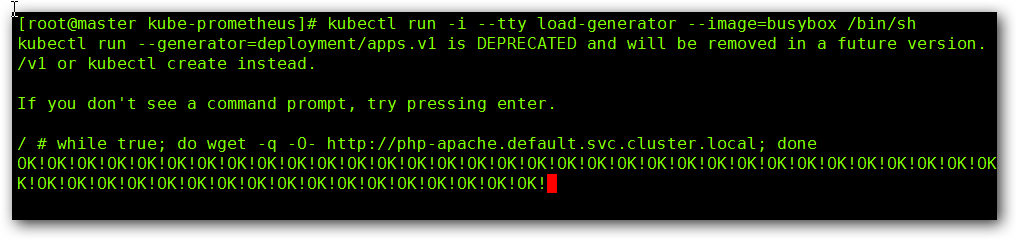
增加负载,查看负载节点数目
两种方式:
1.命令行创建:
创建测试POD:
kubectl run -i --tty zuolaoshi --image=busybox --image-pull-policy='IfNotPresent' /bin/sh
执行命令:
while true; do wget -q -O- http://hpa-web.default.svc.cluster.local; done
2.副本控制器创建:
cat test.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ceshi
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ceshi
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ceshi
spec:
containers:
- name: ceshi
image: docker.io/busybox
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ['sh', '-c', 'while true; do wget -q -O- http://hpa-web.default.svc.cluster.local; done']
资源限制 - Pod
Kubernetes 对资源的限制实际上是通过 cgroup 来控制的,cgroup 是容器的一组用来控制内核如何运行进程的相关属性集合。针对内存、CPU 和各种设备都有对应的 cgroup
默认情况下,Pod 运行没有 CPU 和内存的限额。 这意味着系统中的任何 Pod 将能够像执行该 Pod 所在的节点一样,消耗足够多的 CPU 和内存 。一般会针对某些应用的 pod 资源进行资源限制,这个资源限制是通过resources 的 requests 和 limits 来实现
spec:
containers:
- image: xxxx
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: auth
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
resources:
limits:
cpu: "4"
memory: 2Gi
requests:
cpu: 250m
memory: 250Mi
requests 要分配的资源,limits 为最高请求的资源值。可以简单理解为初始值和最大值
资源限制 - 名称空间
1、计算资源配额
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: compute-resources
namespace: zuolaoshi
spec:
hard:
pods: "20"
requests.cpu: "20"
requests.memory: 100Gi
limits.cpu: "40"
limits.memory: 200Gi
2、配置对象数量配额限制
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: object-counts
namespace: zuolaoshi
spec:
hard:
configmaps: "10"
persistentvolumeclaims: "4"
ReplicaSet: "20"
secrets: "10"
services: "10"
3、配置 CPU 和 内存 LimitRange
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: mem-limit-range
spec:
limits:
- default:
memory: 50Gi
cpu: 5
defaultRequest:
memory: 1Gi
cpu: 1
type: Container
default 即 limit 的值
defaultRequest 即 request 的值